YouTube
0:00 Electricity and Materials
0:37 Conductors and Insulators
1:10 What is a semiconductor?
1:39 Principles of Semiconductors
Electricity and Materials


In this article, we will talk more about the relationship between electricity and materials.
Please read this article to the end to understand the differences between conductors, semiconductors, and insulators, and to gain a better understanding of the principles of semiconductors.
Electricity and Materials
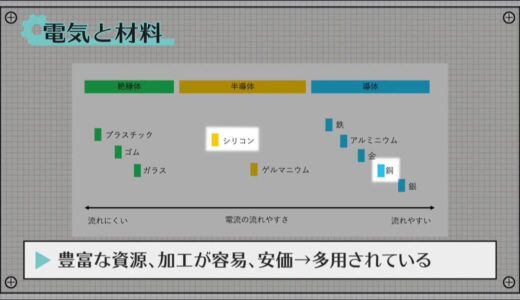
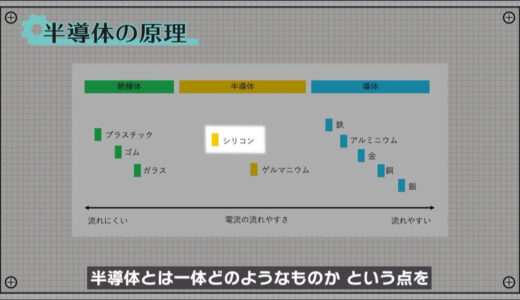
Not all materials can conduct electricity, but they are divided into three major categories according to their ease of flow: conductors, semiconductors, and insulators.
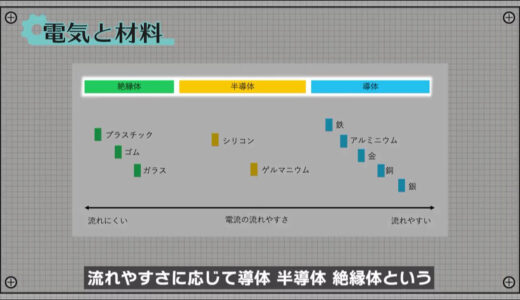
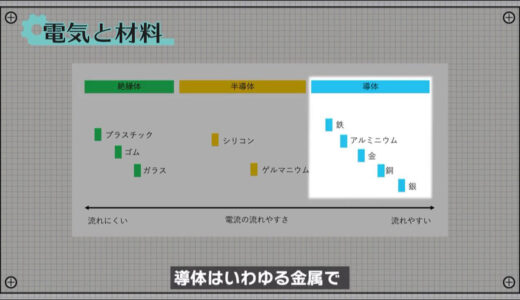
Conductors are so-called metals, while insulators are materials such as glass or plastic.
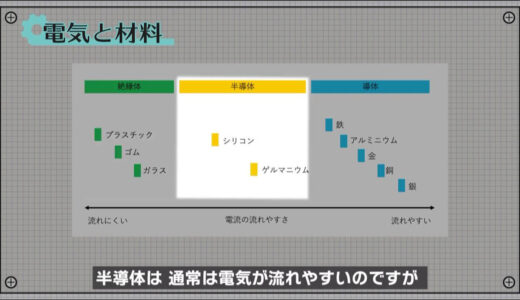
Semiconductors have a dual nature in that they normally conduct electricity easily, but when mixed with another material, electricity passes through them more easily.
Copper and silicon, in particular, are widely used in the electronics industry because of their abundant resources, ease of processing, and low cost.
Conductor and insulator
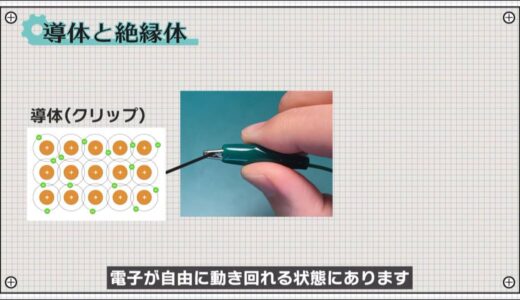
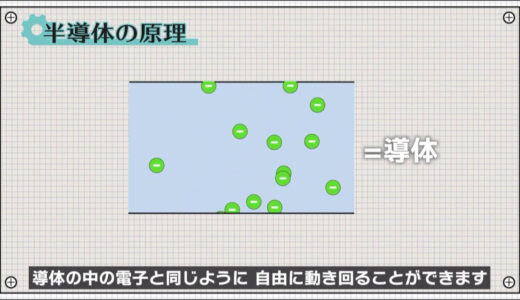
The difference between easy and difficult passage of electricity lies in the degree to which there are electrons that can move around freely.

Taking the alligator clip as an example, the clip part, which is a conductor, is in a state where atoms share the pathway of electrons and electrons can move around freely.
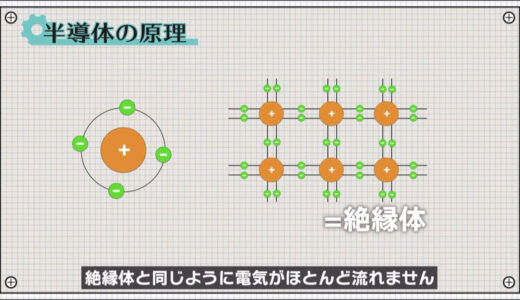
. On the other hand, this insulator, the rubber cover part, is so strongly bound to the nucleus that the electrons cannot move around.
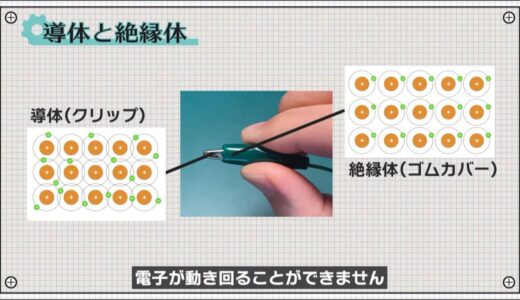
To conduct electricity through an insulator, a force greater than this binding force must be applied, so a large voltage is required.
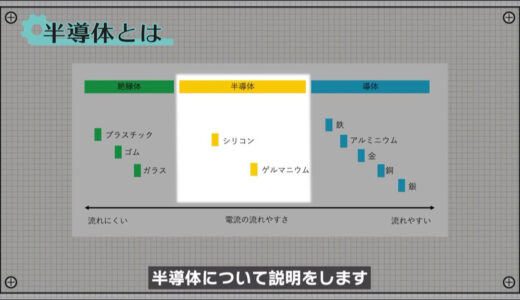
What is a Semiconductor?
Next, I will explain about semiconductors, which can be said to play a leading role in the world of electronics.
Originally, a component called a vacuum tube was used to control electricity, but when the semiconductor transistor was developed in the 1940s, it quickly spread throughout the world because it was so small in size and could be made at low cost.

For example, it is used in many of these components just in the works created in this Electronics Basics.
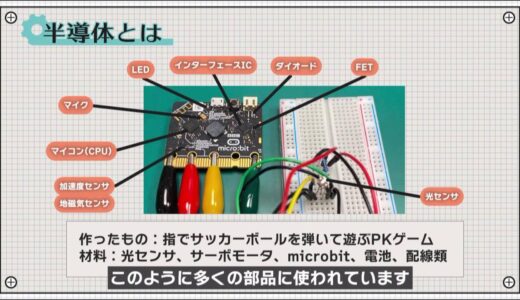
Principles of Semiconductors
Next, I would like to pick up silicon, a typical semiconductor, and explain what exactly a semiconductor is, using a diagram.
Silicon has four electrons in the outermost layer, and the atoms are strongly bound to each other, sharing one electron each.
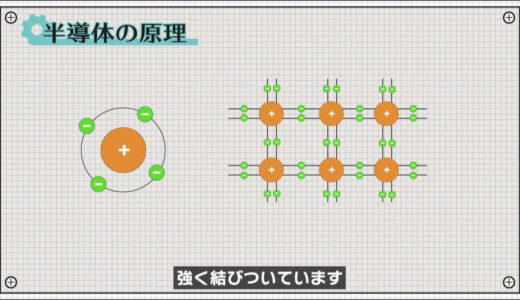
At this time, there are no electrons that can move around freely, so little electricity flows through it, just as it does in an insulator.
If we place an atom with the five outermost electrons, such as phosphorus, the picture changes dramatically.
Since silicon has four electrons and phosphorus has five, there is one extra electron that phosphorus has.
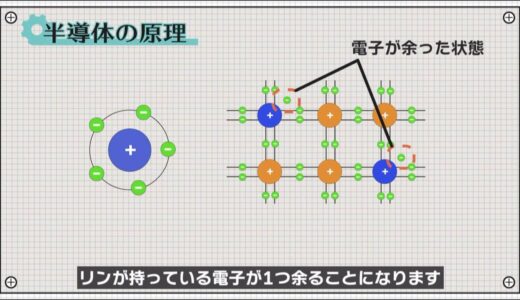
Since these electrons are not bound anywhere, they are free to move around just like electrons in a conductor.
On the other hand, if you bring in an atom with three outermost electrons, as in boron, you now have a space that is missing one electron.
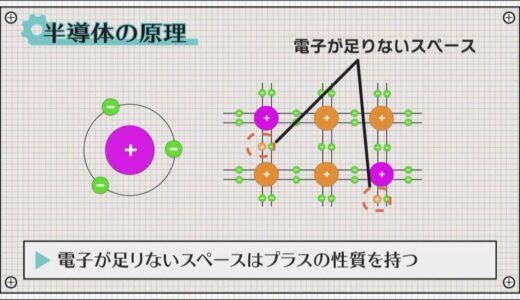
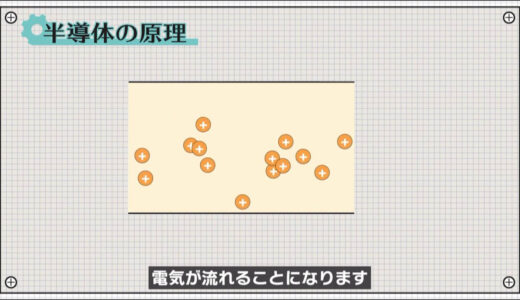
This free space is unstable and attracts electrons in an attempt to create a stable state, which is a positive property.
This empty space is called a hole, and when an electron is attracted to this space, a hole is created where the electron was originally located.
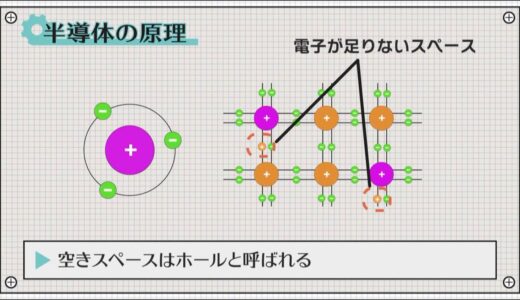
As this is repeated, the hole gradually moves to the negative side, which causes electricity to flow.
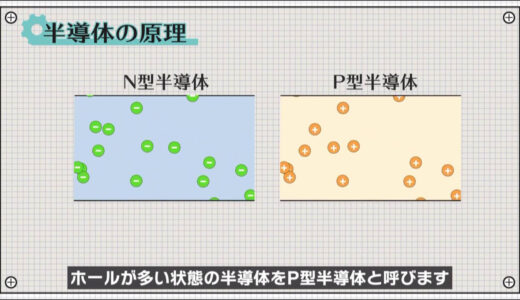
A semiconductor in an electron-rich state is called an N-type semiconductor and a semiconductor in a hole-rich state is called a P-type semiconductor.
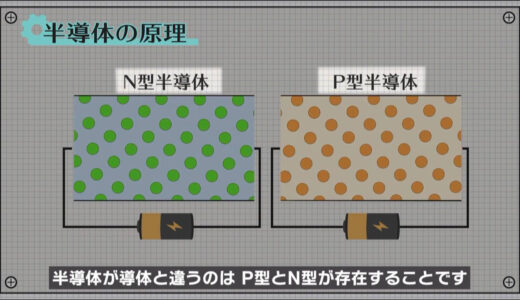
Each of these conductors conducts electricity well when voltage is applied, but what differentiates semiconductors from conductors is the existence of P-type and N-type conductors.
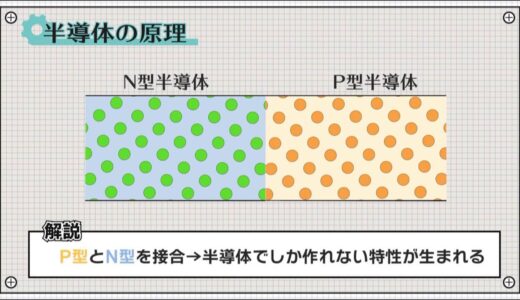
These can be joined and used next to each other to create interesting characteristics that can only be created with semiconductors The first is the “semiconductor”.
And that is the reason why semiconductors have become so popular.
I would like to explain this in the section on electronic components.
summary
In this issue, we have explained in detail the differences between conductors, semiconductors, and insulators respectively, for those who are not sure what exactly a semiconductor is.
Once you understand the difference between conductors, semiconductors, and insulators, and have a better understanding of the principles of semiconductors, you will be able to enjoy electronic construction more.
This site also provides other videos and articles to help beginners learn electronics construction systematically from zero, including explanations of the minimum knowledge and tools they need to acquire.

 Start electronics
Start electronics