YouTube
0:00 Opening
0:16 CPU Specifications
0:54 Built-in Module
1:26 Interface
2:25 Programming
3:04 Summary
Features of Microcontroller Boards|Technical


In this article, we will explain how to choose a microcontroller board according to its application, for those who understand the characteristics of microcontroller boards but are not sure which one to choose in the end.
In the previous article, “[Introduction to Electronic Construction] Features of Microcontroller Boards and How to Select One,” we provided basic information, so we recommend that you take a look at that article first.
By reading this article, you will know how to choose the right microcontroller board for your application, and you will not have to worry about which one you should choose now.
The microcontroller board we have selected for this project is shown below, so please use it as a reference in selecting a board.
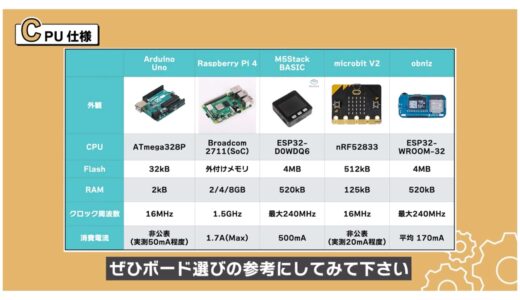
We will now explain each specification as we compare them.
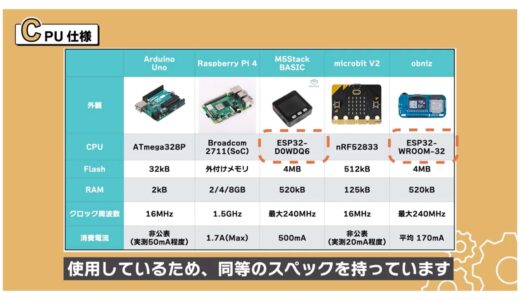
CPU Specifications
First, we will compare the specifications around the CPU.
Below is a summary of the CPU and memory sizes used, which shows that the Raspberry Pi 4 has by far the highest specifications, to start with.
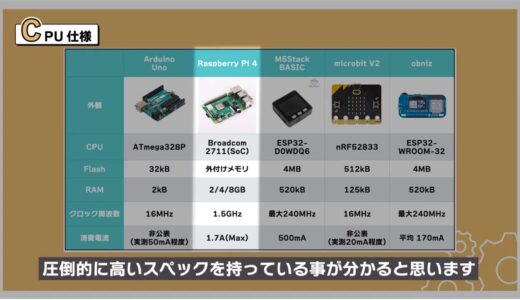
On the other hand, however, the current consumption is high, so a power supply with a large current capacity may be required, which is a bit of a hurdle to use.
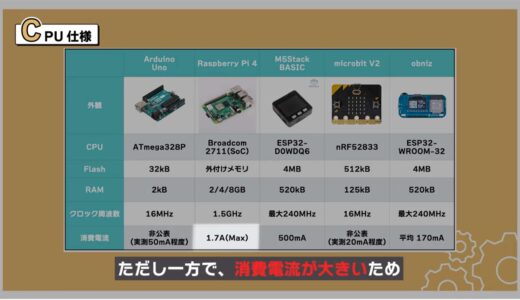
If you do not need that many specs and want to reduce current consumption, Arduino Uno or microbit would be easier to use.
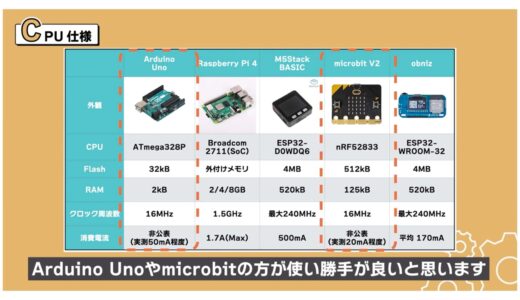
In addition, M5Stack BASIC and obniz use the same ESP32 series, so they have equivalent specifications.
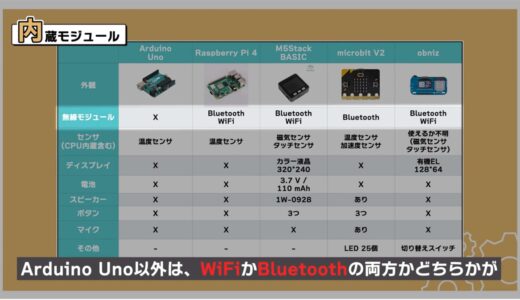
Built-in Module
Next is a comparison of the built-in modules.
As for the wireless modules, which are probably the biggest concern for most people, all but the Arduino Uno have either WiFi or Bluetooth, or both.
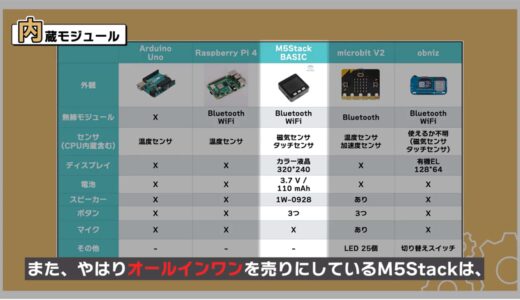
Also, the M5Stack, which is still selling an all-in-one system, is found to have by far the most extensive lineup of sensors and modules.
Next, microbit and obniz are also fair to good.
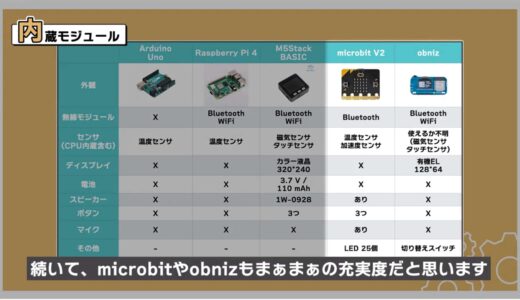

- m5stack
- microbit
- obniz
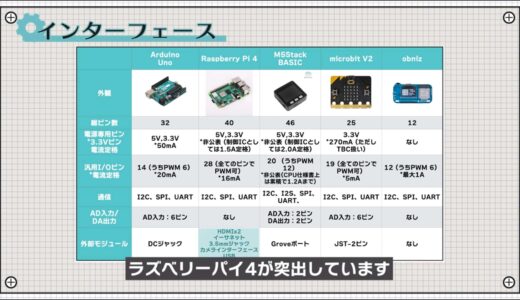
interface
Next, we will discuss the interface.
Looking at the input/output products, you can see that many boards have a dedicated power supply pin, either a 5V pin or a 3.3V pin.
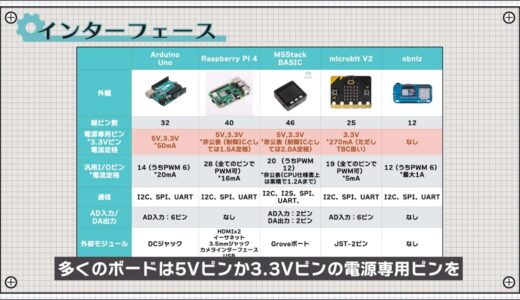
As explained in the video “[Basic Electronic Works] Two Power Supply Methods to Learn from Microcontroller Board Power Supply Pins|Introduction to Practical Electronic Circuits with LTspice”, the amount of current that can flow at 3.3V depends greatly on the conversion method from 5V to 3.3V.
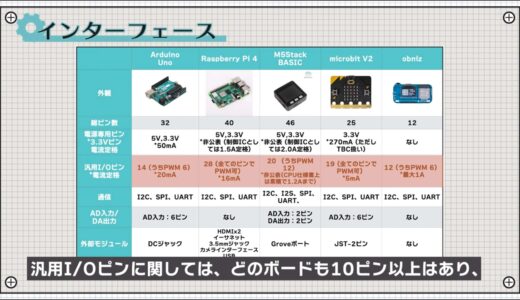
As for general-purpose I/O pins, all boards have at least 10 pins, and you can see that PWM output is also supported by multiple pins.
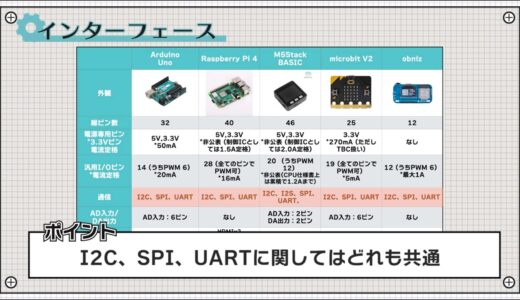
The same communication method with external modules is also common, with I2C, SPI, and UART.
Each board has a different policy regarding analog inputs and outputs, and in particular, having analog outputs is a feature unique to the M5Stack.
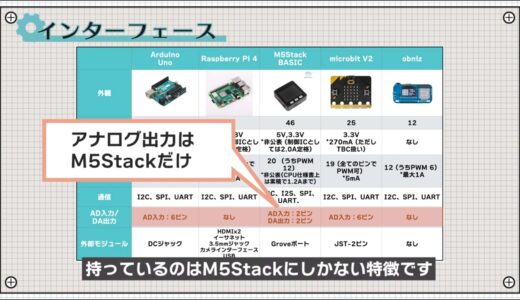
The Raspberry Pi 4 is prominent when it comes to the type of external module interfaces.

programming
Finally, we compared them from a programming perspective.
Python, the most popular programming language, can be used with the following three microcontroller boards.
- Raspberry Pi 4
- M5Stack BASIC
- microbit
Block programming, popularized by Scratch, is also available on most boards, including the Raspberry Pi 4.
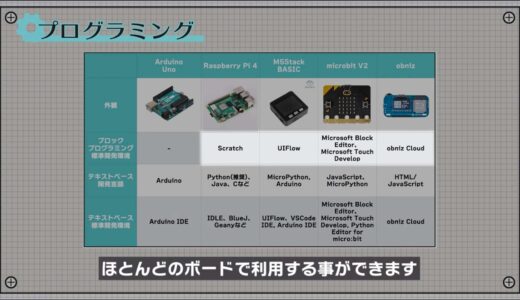
This area depends on what language you want to learn and whether you prefer block or text-based programs.

If you are a complete beginner in programming, you can try any board and start with a block program.

summary
In this issue, we have compared microcontroller boards in a slightly more technically in-depth manner.
We have also created a table summarizing the above, which can be found at the URL below.
http://start-electronics.com/basic/spec-matome/
The information presented here is based on my own research and may be out of date due to updates, etc. Please use it only as a reference.

 Start electronics
Start electronics 



